In medical practice, it is customary to classify baldness into several types depending on the nature of the clinical picture. Cicatricial alopecia is a rare disease. With this form of baldness, affecting mostly women over 40 years old, hair follicles are destroyed, and scars are formed on the scalp. Alopecia of the cicatricial type is difficult to treat.
The exact reasons for the development of cicatricial alopecia remain unknown. It is established that the pathology is not due to heredity. but the disease can occur against the background of genetic abnormalities:
- ichthyosis (diffuse destruction of the scalp),
- impaired skin development,
- abnormal follicular development and more.

The risk zone for cicatricial alopecia includes people diagnosed with infectious and other inflammatory pathologies: syphilis, tuberculosis, psoriasis, versicolor and others.
Mechanical damage to the skin of the head can also lead to the appearance of the disease: injuries, burns, exposure to chemicals.
Important! Baldness of this type is due to the replacement of normal tissue with connective or atrophic skin changes.
Damage to the cover of the head leads to these violations. As a result of such exposure, local tissues are inflamed. Further, the damaged skin is covered with pinkish granulations.
At the final stage of the development of pathology in the problem area, areas consisting exclusively of connective tissue are formed. Inside the latter there are no blood vessels feeding the follicles. Due to the lack of oxygen, the latter die off, as a result of which hair growth stops at the problem site.
 Cicatricial alopecia is divided into:
Cicatricial alopecia is divided into:
- Primary. In this form, baldness develops immediately after the destruction of the hair follicle.
- Secondary. Pathology arises from the progression of the inflammatory process. Secondary baldness is not treatable.
Depending on the causative factor cicatricial alopecia develops by type:
- exfoliating panniculitis,
- eosinophilic pustular folliculitis,
- follicular degeneration syndrome,
- Broca's pseudopelade,
- decalvating folliculitis,
- flat follicular lichen.
There is also an x-ray form of pathology. This disease develops in the treatment of fungal infections. X-ray therapy causes thinning of the scalp and damages the skin.
According to localization, cicatricial alopecia is divided into frontal (forehead area) and androgen-dependent (mainly crown).
Clinical picture
The nature of the clinical picture in cicatricial alopecia is determined by the type of factor that provoked the development of the disease. The only reliable signs of the presence of pathology are baldness of a separate part of the head and inflammation of local tissues. The remaining symptoms may be of the following nature:
- pain syndrome,
- intense itching and burning,
- swelling and redness of the skin,
- peeling.
Important! Hair with cicatricial alopecia falls out immediately after exposure to the causative factor or with time as the inflammatory process progresses.
Diagnostic methods
 The purpose of diagnostic activities carried out in cicatricial alopecia, is to identify the causes of the disease. Alopecia of this type is often accompanied by the following pathologies:
The purpose of diagnostic activities carried out in cicatricial alopecia, is to identify the causes of the disease. Alopecia of this type is often accompanied by the following pathologies:
- mycosis,
- pustular and bullous dermatosis,
- keloid inflammation of the follicles,
- parasitic or bacterial infections,
- sarcoidosis and others.
The basis of the diagnosis is a biopsy of tissues collected from the problem area. The method allows you to explore the process of scarring of the skin and to identify the current stage of destruction of hair follicles.
Trichoscopy and phototriscopy give more accurate results. Both methods allow you to set:
- skin type
- condition of hair follicles,
- the density and the ratio between healthy and damaged hair,
- current alopecia phase.
Trichoscopy and phototriscopy are also carried out in order to exclude other forms of alopecia.
The goal of treating cicatricial alopecia is to eliminate the provoking factor and slow down the balding process. The scheme of treatment is selected based on the causes of the development of pathology.
 With mycoses, dermatoses and some other diseases Reception of the following medicines is shown:
With mycoses, dermatoses and some other diseases Reception of the following medicines is shown:
- antimalarial,
- immunosuppressants,
- antibacterial,
- thiazolidinedione (antidiabetic drugs).
In addition to taking systemic drugs, it is necessary to regularly treat problem areas of the skin with ointments, which include corticosteroids and cyclosporin. It is also recommended to apply to the affected areas medications that inhibit or stimulate (depending on the indications) local immunity.
It is possible to restore the work of the follicle with the primary form of alopecia. If the bulb tissues remain viable, an antihypertensive drug is injected directly into the problem areas. This medicine stimulates hair growth.
Cicatricial alopecia requires long-term treatment. Drug therapy is designed to stop hair loss and eliminate the associated symptoms. In addition, it is important to treat comorbidities, which are accompanied by balding of different parts of the body.
Important! Even with the stabilization of the head condition, the possibility of recurrence of cicatricial alopecia remains several years after the end of treatment.
 If the disease does not progress for a year or more, hair replacement surgery is prescribed.
If the disease does not progress for a year or more, hair replacement surgery is prescribed.
The method, known as follicular micrografting, involves the transplantation of donor skin with healthy follicles to problem areas. After such an operation, the skin area of the head is reduced.
Prevention
Due to the fact that the true cause of the development of cicatricial alopecia has not been established, Doctors have not yet developed specific prevention methods to prevent baldness of the head. To reduce the likelihood of this disease, it is recommended to strengthen the hair through vitamin complexes and special masks. In addition, the pathologies that cause tissue inflammation should be treated promptly.
Cicatricial alopecia does not pose a threat to human life and health. In this case, the pathology worsens the patient's appearance, which leads to the development of psychological disorders. Treatment of cicatricial alopecia is not able to prevent the recurrence of the disease.
Useful videos
Types of baldness: gnezdny, androgenic (androgenetic), cicatricial, focal, diffuse, total.
Alopecia - causes, characteristics and treatment.
Causes
Sometimes the disease occurs due to frequent exposure to X-rays. Foci of hair loss appear unevenly on the head and have an irregular shape. In places of baldness, there is atrophy of the skin, which is not accompanied by any peeling or crusting. Over time, scar tissue forms on the affected areas, due to which the hair follicles are completely destroyed.
Alopecia cicatricial is rather difficult to cure due to the fact that the causes of this type of baldness can be different and it is not always possible to determine them quickly.
 Cicatricial type of hair loss in the photo.
Cicatricial type of hair loss in the photo.
Types of scar alopecia:
- Primary cicatricial alopecia (arising from the destruction of the hair follicles during the inflammatory process).
- Secondary cicatricial alopecia (there is abundant hair loss due to the active progression of the disease and various injuries).
In the secondary type of the disease, follicle destruction occurs instantaneously and is an irreversible process.
Factors contributing to the occurrence of cicatricial alopecia:
- neoplasms in the body,
- genetic predisposition (eg, pigment incontinence),
- infectious diseases (syphilis, tuberculosis, leprosy, etc.),
- burns, both chemical and thermal,
- mechanical damage to the scalp,
- Lassuer-Little syndrome,
- chronic diseases.
 Destruction of the hair follicles during inflammation.
Destruction of the hair follicles during inflammation.Note! The disease can occur due to prolonged use of steroid drugs or frostbite.
Diagnostics
Cicatricial alopecia in women of different ages and men should be diagnosed only by a competent specialist. In order to establish an accurate diagnosis, patient complaints will not be enough. It is recommended to perform a biopsy of the scalp skin, which will determine not only the stage of destruction of the hair follicles, but also the stage of scar formation. For more data, doctors recommend making a trichogram, thanks to which you can determine the condition and density of hair. For unknown reasons for the formation of such a pathology, patients should contact a dermatologist and therapist who will prescribe a more extensive examination.
Diseases associated with pathology:
- lupus erythematosus,
- sarcoidosis
- lichen planus
- pustular diseases, etc.
 Trichogram of hair is one of the ways to diagnose alopecia.
Trichogram of hair is one of the ways to diagnose alopecia.The basic principle of treating scar alopecia is to stop further scarring of the skin, as well as getting rid of the cause of the formation of the disease. Rehabilitation of patients with this pathological condition begins with a detailed visual examination, determining the current state of health and the detection of chronic diseases and injuries that could contribute to the development of cicatricial alopecia. The only way to relieve the patient from baldness is surgery, due to which the scar will be removed, and in its place the full-fledged skin that contains fatty tissue, blood vessels and hair follicles is replaced by doctors.
At the early stage of the development of the disease, the problem can be solved in a medical way. Such therapy is able to stop excessive shedding of hair. Quite often, doctors prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics, as well as immunostimulants. Drug treatment will also be aimed at eliminating the root cause of the disease, so that truly positive results can be achieved.
Before you use medications, you should consult with your doctor.
A less painful and dangerous treatment option for cicatricial alopecia is using the hair system. This method of hair replacement is very popular all over the world, because thanks to it you can quickly and permanently get an attractive look. The hair system is the attachment of natural hair by hand to a thin silicone base on the surface of the patient's head. The length, shade, structure and density of the hair is determined individually.
 Method of treating baldness problems.
Method of treating baldness problems.
Cicatricial alopecia brings a lot of inconvenience, lowers self-esteem and can completely separate a person from the outside world. To avoid such a situation, it is worth contacting a qualified specialist who will accurately determine the initial cause of the rapid hair loss and prescribe an effective treatment. If you find a pathological disease, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Establishing diagnosis
To determine the specific type of alopecia and outline the stages of treatment, special diagnostic tests are carried out, whose results are evaluated by your doctor:
- Visual inspection of the affected area.
- Blood test for hormones, syphilis, for biochemical parameters. General blood analysis.
- Rheoencephalography (REG) - to determine the speed of blood flow in the vessels of the cranial region.
- Hair microscopy - to study the characteristic changes in the hair structure.
Below you can see the photo, what looks like cicatricial alopecia:



Causes of development
Cicatricial formations are a consequence of a flowing or past illness and are secondary. The culprits of their appearance on the skin surface, as a result of hair loss, may be physiological causes, as well as diseases of infectious and non-infectious nature:
- Transferred physical injuries and burns.
- Hereditary disorder and hair development defects.
- Chronic diseases.
- Rare forms of infections.
Symptoms and stages
Cicatricial Alopecia develops over a long time and can behave differently:
- In some cases, people almost immediately begin to notice itching, burning, and feel discomfort in the affected area.
- In other situations - the scars can develop unnoticed, without severe symptoms.
Regardless of whether the disease progresses markedly, the clinical picture looks the same: the inflammatory process begins, leading to the death of the hair follicles and the formation of connective tissue material in their place. It can be accompanied by unpleasant sensations on the skin, blisters with fluid, which are subsequently replaced by smooth scars. Follicles die completely and are no longer able to function.
Preparations and procedures
 First of all, means and procedures are assigned to help eliminate the pathological effects and the primary causes of scar alopecia, to prevent its further spread.
First of all, means and procedures are assigned to help eliminate the pathological effects and the primary causes of scar alopecia, to prevent its further spread.
At an early stage (when the foci did not have time to heal), regular medication can stop hair loss. Alopecia, manifested due to inflammation of the hair follicles, for example, when syciformis folliculitis or lichen planus, is treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics and immunostimulants. Corticosteroids can be prescribed - in the form of topical creams and injections into the affected area of the skin.
- Psychotropic and nootropic drugs (sibazon, azafen, nootropil).
- Vitamins (A, E, multivitamins, including those containing trace elements), phytin, biotin.
- Immunocorrective drugs (decaris, methyluracil, T-activin).
Folk remedies
To slow down the process of baldness, you can use traditional medicine. If you use the right recipes for a particular type of illness, treatment can be effective. In some cases, the doctor himself advises folk remedies, for example, if you are allergic to medication.
An effective remedy in eliminating alopecia is garlic. - due to the high content of vitamin C and essential oils. The use of garlic-based recipes gives a disinfecting effect and restores the hair roots.
There are other means of a particular action:
- Broths of sea buckthorn, burdock roots - for nourishing the skin with essential substances.
- Alcohol infusion of calendula - taken by mouth 2 times a day.
- Broths from a linden and a camomile - solution is used for rinsing hair.
Hair transplantation
In the later stages of alopecia, patients are offered hair transplants.
The follicular transplantation method is concluded in the removal of donor follicles and their implantation in baldness sites. Hair from different parts of the body is used for the operation..
The method of skin grafting from the occipital part of the frontal and parietal lobes allows you to restore uniform hair growth, especially with focal alopecia.
Hair loss is a common phenomenon in humans, regardless of age or gender.The characteristics and effects of this disease are also different, as are the possible causes. Treatment of cicatricial alopecia is a long and serious process. Methods and preventive courses are prepared individually for each patient. therefore It is extremely important to follow the recommendations of a specialist and treat them responsibly..
Scar formation process
- The impact of a negative factor on the fabric.
- The emergence of the inflammatory area in which the cells are healing tissue and collagen, restoring it to the state of the scar.
- After the formation of the scar, the death of the hair follicle begins.
In some cases, with timely consultation with a specialist, the process of scar formation can be reversible. Finally the scar is formed only after 4-6 months from the beginning of the pathological process.
General recommendations
If a disease that causes alopecia is suspected, or if a baldness symptoms occur, it is important for the patient to consult a specialist in time. Detection of diseases in the early stages will help to avoid negative consequences. About scar alopecia it is important to know:
- Cicatricial alopecia with a favorable course deactivated during the year after the start of the process.
- Care for the hair and scalp requires careful and neat. It is recommended to use mild detergents. The frequency is chosen individually, but at least once a week.
- Required reception prescribed drugs and vitamins.
Cicatricial alopecia is an unpleasant disease that has an unfavorable prognosis in its form. The sooner the doctor visits, the less adverse the disease will have.
Causes of baldness
 Each person grows bald in different ways, but due to the high prevalence of alopecia, several patterns can be traced in its appearance. Usually, androgenicbaldness begins to manifest itself immediately after the end of puberty and by the age of thirty it is finalized. Its main cause can be called the heredity of man.
Each person grows bald in different ways, but due to the high prevalence of alopecia, several patterns can be traced in its appearance. Usually, androgenicbaldness begins to manifest itself immediately after the end of puberty and by the age of thirty it is finalized. Its main cause can be called the heredity of man.
With an increase in the concentration of male hormones in a person’s blood, the hair on his head begins to thin out and be replaced by a fluff, which gradually loses its color and becomes thinner. It manifests itself first in both temples, then smoothly moves to the crown. There, too, hair begins to thin. With the growth of these areas, they are gradually merging into one bald spot.
Total baldness provoked mainly by external factors. It can be poisoning with various chemical elements - thallium, bismuth, arsen (arsenic), acid vapors (for example, boric acid), fungal diseases of the scalp, radiation procedures. If drugs that slow down cell growth are used as treatments for tumors, this can also lead to the death of the bulbs and hair loss.
 Reasons diffusealopecia hormonal changes in the human body during pregnancy or puberty, stress, lack of beneficial trace elements, such as iron or B vitamins, bad habits and contraceptive use can be made. In case of hormonal disturbance, it is temporary, disappearing after it returns to normal. In other cases, it requires intervention.
Reasons diffusealopecia hormonal changes in the human body during pregnancy or puberty, stress, lack of beneficial trace elements, such as iron or B vitamins, bad habits and contraceptive use can be made. In case of hormonal disturbance, it is temporary, disappearing after it returns to normal. In other cases, it requires intervention.
Focal baldness due to the presence in the body of a person suffering from autoimmune processes. This disease regards follicles as alien organisms. Most common in dark-haired men and women. The main reasons are:
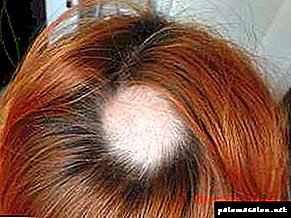 Heredity (more than a quarter susceptible have family pathology).
Heredity (more than a quarter susceptible have family pathology).- Stress and severe mental turmoil.
- Incorrect work of some glands of the body - adrenal glands, pituitary and thyroid.
- Chronic diseases - caries, rhinosinusitis.
- Blood supply problems due to changes in viscosity and blood flow rate.
- Viral infections.
In men, it can also manifest itself as a lack of mustache and beard growth.
Seborrheic hair loss
With increased sebum secretion A disease such as seborrhea or seborrheic dermatitis may occur on the surface of the head under the hair. It often causes thinning, damage and loss of hair in those areas that affects.
 The causes of its occurrence can not be accurately determined. Many experts agree that this is a complex of genetic causes, diseases associated with the endocrine glands, hormonal changes and the influence of harmful environmental factors. The alleged causative agent of seborrhea is a special type of fungus - Malassezia furfur, which is present in most people in the microflora of the scalp (may be about half of its microorganisms).
The causes of its occurrence can not be accurately determined. Many experts agree that this is a complex of genetic causes, diseases associated with the endocrine glands, hormonal changes and the influence of harmful environmental factors. The alleged causative agent of seborrhea is a special type of fungus - Malassezia furfur, which is present in most people in the microflora of the scalp (may be about half of its microorganisms).
Alopecia occurs in about a quarter of cases of seborrhea. Its development is accompanied by increased secretion of sebum under the hair, because of which they become oily shine and stick together, and eczema on the skin. As a result, the skin pores become clogged, the hair does not receive sufficient nutrition and gradually becomes thinner. The affected areas are mostly either at the edge of hair growth, or from the frontal to the back of the head. They are always surrounded by dense rows of healthy hair.
Alopecia Treatment
 First you need to find out the exact cause.. Alopecia, caused by external factors or skin diseases, is treated completely differently than caused by hereditary or hormonal causes.
First you need to find out the exact cause.. Alopecia, caused by external factors or skin diseases, is treated completely differently than caused by hereditary or hormonal causes.
Cicatricial alopecia is curable only by hair transplantation. Before performing it, it is necessary to surgically remove the affected areas of the scalp and wait until the wounds have completely healed. Bulbs are transplanted from other skin areas covered with healthy hair, such as the chest, back, or buttocks. Hair from the legs for such a transplant is not suitable.
Methods for treating non-scarring forms
Non-cicatrical alopecia has several treatments..
- Preparations Finasteride and Minoxidil, stimulating hair growth. It is necessary to use them strictly adhering to the course and not interrupting it, since it threatens with an extensive relapse.
- Physical therapy, if there are no damage to the scalp - massaging the skin, Darsonval, electrical and laser effects, the use of stimulating and irritating the skin means (an example of such means can be pepper tincture).
 Drugs for improving blood microcirculation and speeding up metabolic processes in the affected areas. These include Heparin, Aminofillin, Trenal and others.
Drugs for improving blood microcirculation and speeding up metabolic processes in the affected areas. These include Heparin, Aminofillin, Trenal and others.- Maintain a healthy lifestyle and eliminate harmful factors such as stress, improper and irregular nutrition, failure to follow the daily regimen and the cycle of sleep and wakefulness.
- With the detected autoimmune process of the body, aimed at the hair follicles, glucocorticosteroids should be used - at the lesion site or in particularly neglected and malignant cases in tablet form.
- The course of vitamin complexes, which include in its composition and trace elements.
You can try to cure baldness with folk remedies. Here various decoctions, ointments and tinctures of such medicinal plants as burdock and burdock, with the addition of honey and alcohol solutions, are useful. You can use crushed sea salt as a preliminary peeling. It should be rubbed into the scalp before washing, carrying out a peeling and peeling of dead skin, stimulating the growth of new follicles and blood circulation.
Brief description of the problem
What is cicatricial alopecia? Cicatricial alopecia is a type of baldness that has some differences from other forms of hair loss. The main difference is a very unfavorable course and prognosis of the disease.
Disease affects the hair follicleswhich are gradually being destroyed.

On the damaged areas of the scalp there are seals - scars consisting of connective tissue.
These seals overlap the hair follicles, as a result follicle cannot perform its function, hair stops growing.
This type of baldness is quite rare.
It is noted in about 3% of patients who went to the doctor with the problem of hair loss.
Causes of illness
The causes of cicatricial alopecia are diverse and numerous. Often this problem may indicate a serious illness, problems in the work of internal organs and systems.
Among the factors of cicatricial alopecia development include:

- Congenital causes. Due to the genetic predisposition of the skin of the scalp develop from the first days of a child's life.
- Infectious pathologiessuch as syphilis, tuberculosis.
- Oncological diseases (benign and malignant tumors), the use of chemotherapy and other methods of their treatment. Alopecia in this case does not always develop, it all depends on the intensity and duration of exposure to chemicals on the body.
- Mechanical damage scalp (burns, injuries, frostbite).
- Pathology autoimmune character.
- Diseases of the scalp (eg, lichen).
Signs of cicatricial alopecia
Clinical manifestations of the disease, regardless of the cause of its occurrence, are as follows.:
- The appearance on the scalp of the delineated areas of baldness, which at first are of minor size.
- Over time, these areas increase in size, become more visible.
- The patient complains of discomfort in the area of injury. He is itching, burning, painful sensations over time.
- In the affected areas of the skin, inflammatory reactions, redness, ulcers and sores occur, the skin becomes more dry and flaky. However, there are cases when such manifestations are not observed, the skin remains smooth without any signs of damage.
- After some time, the inflammatory reactions subside, the complete absence of hair is marked on the affected areas.
See what cicatricial alopecia looks like in the photo:





Pathogenesis of the disease
Cicatricial alopecia develops gradually, in the initial stages of the disease its symptoms may be minor, barely noticeable.
- At the first stage, damage to the upper layers of the skin due to the negative impact of damaging factors.
- Cells exposed to such exposure begin to secrete biologically active substances.
- Foci of inflammation appear on the skin., itching, feeling of dry skin.
- In the damaged areas of the skin, a substance is actively synthesized - collagen, with accumulation of which a scar of a reddish hue forms. Symptoms of the disease become irreversible.
- The scar becomes more pale, gradually hardens, thickens (this stage may have different duration: 1-3 months.)
- At the last stage, the hair follicles are destroyed.they atrophy, can not perform the functions of the production of hair. On the scalp, scars are transformed into hard scars, which can be seen not only to the touch, but also visually.
Treatment of cicatricial alopecia
The effectiveness of treatment depends primarily on the stage of the disease. In the initial stages development of baldness can stop this process, eliminating the main cause of its development.
In this case only surgery will help. This is a hair transplant using donor skin. For more information about modern methods of transplantation, including non-invasive methods and the price of this procedure, you can find on our website.

However, here forecasts are ambiguous: Since the patient's skin is covered with scars, dense formations in which blood circulation is impaired, donor grafts may not settle down.
Cicatricial Alopecia - one of the most serious types of baldness. With the disease of this species, there is destruction of the hair follicles, complete loss of hair in the affected areas.
Traditional methods are powerless here. Ointments and creams, drugs, the expected effect will not give. For successful treatment, surgery is necessary, and, of course, the elimination of the cause of the disease.
Description and clinical picture of the disease
Cicatricial alopecia refers to a polyetiological disease. When it happens permanent hair loss due to the death of the follicle during the course of an inflammatory or other pathological process.
The ending of the disease is alopecia and scarring. After baldness due to this ailment, it is impossible to fully restore the old hair - hair follicles are completely destroyed or can not fully perform their function.
Regardless of the cause of the disease, the clinical picture remains characteristic. First of all, baldness begins in small areas, the affected area increases gradually. At the same time, symptoms such as burning, pain, and itching begin to trouble the sick person.
Scarring of the skin areas takes place in stages:
- Damaged tissue.
- The cells begin to secrete a biologically active substance.
- The process of inflammation begins and collagen-producing cells are attracted to the damaged area.
- Collagen synthesis begins, which leads to the formation of a "young" scar.
- After 1-3 months, the scar matures, becomes paler and less protrudes above the skin surface.
- At the last stage, which takes from a third of a year to 12 months, the scar passes the final transformation - the vessels from the scar disappear, and the collagen fibers, previously concentrated in bundles, line up in a single line.
But sometimes the disease is accompanied by the development of inflammatory processes - the appearance of sores, peeling, blisters with pus and others, which eventually heal and turn into smooth skin. If, during the formation of the scar, a malfunction has occurred, then the scar may turn out to be convex, hollow, or take the form of a keloid scar.
The causes and forms of the disease
Cicatricial alopecia develops gradually, in several stages, and the causes of the occurrence of the disease may be the following factors:
- malignant or benign tumor,
- inherited disorders and developmental defects (ichthyosis, pigment incontinence and others),
- injuries (burns, wounds, bruises, etc.),
- congenital follicular pathologies,
- radiation exposure
- extreme stages of individual diseases including lupus erythematosus, basal cell carcinoma, lichen planus and others,
- specific infectious diseases (leprosy, favus, tuberculosis, leishmaniasis, and similar).
The condition of the skin depends on the reason why the disease appeared - both scars can remain on it, and cicatricial atrophy of the skin can occur.
To determine the treatment, it is necessary to identify the form of this alopecia. The most common are:
- Little-Lassuer syndrome,
- decalvating folliculitis,
- exfoliating panniculitis,
- flat follicular versicolor,
- eosinophilic pustular folliculitis,
- follicular degeneration syndrome
- Brock's pseudo-pope.
We advise you to read:
Symptoms and diagnosis
 The obvious symptom of the disease is the beginning of baldness on a small skin area. Pathology can develop either gradually (in this case, the clinical manifestations are not immediately noticeable) or quickly (the pathological manifestations progress, and the course of the disease itself is accompanied by desquamation, pain, itching, and similar symptoms).
The obvious symptom of the disease is the beginning of baldness on a small skin area. Pathology can develop either gradually (in this case, the clinical manifestations are not immediately noticeable) or quickly (the pathological manifestations progress, and the course of the disease itself is accompanied by desquamation, pain, itching, and similar symptoms).
The affected area is edged around the perimeter of the dermis, which has a rough structure, and on the periphery of the skin and hair cover remain the same. On the outskirts of the affected baldness zone, viable follicles may remain, recovering with time.
This procedure allows you to identify:
- form of the disease
- the degree of destruction of bulbs,
- what stage is the scarring.
In addition, it is necessary to differentiate cicatricial atrophy from focal - done by examining the boundary of hair loss and the available signs of atrophy of the skin.
1 Causes of cicatricial alopecia

The destruction of hair follicles can occur for the following reasons:
- Traumatic and chemical damage to the scalp: injuries, burns, frostbite, acids and alkalis. When exposed to a direct destructive physical factor on the deeper layers of the skin, the follicles are damaged, the hair falls out, their subsequent growth stops,
- X-ray exposure - X-rays provoke damage to stem cells in the area of the hair follicles,
- Flat hair lichen,
- Autoimmune pathologies: discoid lupus erythematosus, sarcoidosis.
Whatever the cause of cicatricial alopecia, it leads to the formation of a scar in place of the hair follicle, and therefore prevents its restoration and does not give a chance for new hair growth.
The chance of hair regrowth in cicatricial alopecia with cicatricial changes in the follicular zone is extremely small.
2 How to form a scar in the area of the hair follicles

The pathological process in this disease proceeds in stages. There are the following stages in the formation of the scar in the area of the follicles:
1) infiltration stage - accompanied by an active inflammatory process near the follicle and inside it. The cells produce a lot of biologically active substances, inflammatory mediators, fibroblast infiltration occurs.
2) collagen production stage - fibroblasts in the hair growth zone begin to actively produce collagen, replacing normal cells with collagen fibers
3) fibrosis stage - many living, active cells of the follicle begin to be replaced by fibrous tissue, follicle deformity develops, and its death. At this stage, the scar tissue is a reddish color, may somewhat rise above the skin.
4) keloid stage - in place of the hair follicle, a rough, scar tissue forms. It is pale in color, may take the form of a scar, a shallow depression or slightly protrude
If a scar has already formed, hair growth cannot be restored at this point. At the stage of infiltration or the initial production of collagen such a chance is still there.
But since the chance of detecting pathology at the earliest stages is extremely small, the term “scar alopecia” most often characterizes irreversible hair loss.
3 Symptoms

The clinical picture of cicatricial alopecia can begin with a small area of baldness, and as the disease progresses, all large areas of the scalp can be involved in the pathological process.
When cicatricial alopecia, unlike many other forms, together with hair loss, the following symptoms are observed: itching, burning of the scalp, redness, blistering.
In case of chemical, physical and thermal damaging agents, the area of damage of the hair coat corresponds to the zone of impact of the pathological focus, and baldness is clearly associated with this effect.
5 Treatment of cicatricial alopecia
The goal of the treatment of this disease is to prevent the damage of new areas of hair, stop the formation of new scars and eliminate the cause of scar alopecia (if the etiological factor is another disease).
When cicatricial alopecia is very important in time to establish the diagnosis and prescribe treatment. Hair growth at the site of the scar is not restored and the doctor’s task is to preserve healthy areas of the growth zone as much as possible.
Locally may apply:
- corticosteroid ointment
- topical immunomodulators
- vitamin preparations
- retinoids

An injection of glucocorticosteroids, vitamin B12 into the affected scalp is practiced. These procedures can be performed on an outpatient basis.
The mechanism of therapeutic action is the anti-inflammatory, metabolic effect, improving tissue regeneration.
In the treatment of cicatricial alopecia, physiotherapeutic methods of research are actively used:
- laser therapy
- electrophoresis
- photocoagulation
- oxygen-ozone therapy
Ozone activates the redox processes in the body, stimulates the immune system, has anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory effects. The intravenous injection of ozonized physiological solution to patients, autohemotherapy with ozone is practiced.

In order to close the cosmetic defects - areas of scarred skin of the scalp without hair, surgical methods are used - removal of scar tissue and skin grafts with hair follicles.
But transplantation is performed under certain conditions: in the presence of a suitable donor, as well as in the absence of any signs of inflammation in the area being transplanted.
It is not always that the transplant survives successfully in a new place; this is due to impaired blood flow in the transplanted area and the risk of developing immune rejection.
There are painless and non-invasive ways of masking cosmetic defects in cicatricial alopecia - wearing wigs, chignons, special linings of natural or artificial hair.

 First of all, means and procedures are assigned to help eliminate the pathological effects and the primary causes of scar alopecia, to prevent its further spread.
First of all, means and procedures are assigned to help eliminate the pathological effects and the primary causes of scar alopecia, to prevent its further spread. Heredity (more than a quarter susceptible have family pathology).
Heredity (more than a quarter susceptible have family pathology). Drugs for improving blood microcirculation and speeding up metabolic processes in the affected areas. These include Heparin, Aminofillin, Trenal and others.
Drugs for improving blood microcirculation and speeding up metabolic processes in the affected areas. These include Heparin, Aminofillin, Trenal and others.

