
If we are “lucky enough” to encounter such an unpleasant disease as head lice - namely, infection with lice, we may want to learn more about these disgusting creatures.
How many lice grow, how long they live, how fast and how to reproduce?
We will try to understand this question: let's consider the development cycle of head lice from all sides.
general description
Head louse is a small blood-sucking insect parasite that lives only on the human body and feeds on blood.
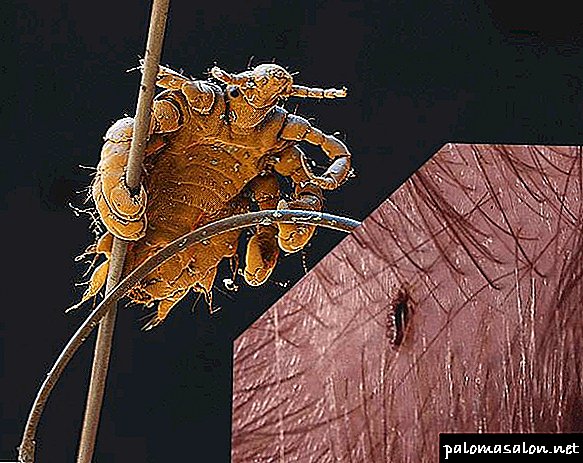
The insect develops very quickly, in just three weeks, thanks to a stable and comfortable living environment.
Stability is ensured by the fact that most individuals spend their entire lives on the body of one personand comfort - the constant availability of food in the public domain (blood).
Every time, before moving on to a new stage of development, lice shed.
This is due to the fact that the chitinous cover does not have time to grow with the body and, simply, is broken.
The molting process takes about 5 minutes.
Definition
Lice - insects that parasitize the skin of mammals. Their body is flattened and includes three sections: head, chest, abdomen. Males are somewhat larger than females. They have piercing-sucking mouth apparatus, which allows sucking blood through small punctures in the epidermis. Do without wings.
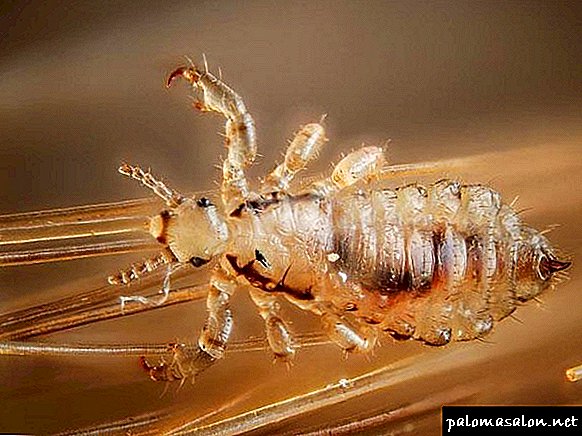

Attention! About 500 species are known to science, but only three of them can live on the human body: dressing, head, pubic. What types of lice are, what is their difference, you will find on our website.
Nits - lice eggs covered with a protective sheath. Represent an elongated white capsule, the size of which does not exceed 1 mm.
These insects are dangerous to health, as they are carriers of various diseases.
general information
Since the louse can not do without food for more than a day, the first bites occur almost immediately after the appearance of parasites on the human hair.
However, the bites of 1 - 2 individuals are insignificant, and usually people do not attach importance to them.
Pediculosis begins to manifest itself only at 3-4 weeks after infection. During this period nymphs of the first generation of lice grow in the hair.

They begin to actively bite the head of a person, causing itching, purulent wounds, spots on the skin and allergic rashes. The life cycle of lice is highly dependent on the lifestyle and habitat of their carrier. Favorable conditions contribute to the fact that on the third week after infection, the second generation of lice already has time to appear in the hair.
Lice life cycle
Lice are species-specific parasites. This means that only people are affected.
Infection is possible in places of large concentrations of people and often occurs where the density of residence is quite high.
Lice infestation was a real catastrophe during times of war, when people were forced to live in barracks.
There are several ways to transmit parasites from person to person:
- Close contact between people, during which insects crawl from an infected person to a healthy one. Often this happens when people sleep in the same bed, as well as during contact games between children.
- Through personal care products such as combs, hoops, hairpins.
- Through clothes. Mainly through objects in contact with the head: hats, hoods, scarves. Parasites can be transmitted through bed linen.
- Due to the high resistance of parasites to hypoxia, they can be transmitted by bathing a large number of people in one pool.
Lice are insects with incomplete transformation. A larva hatches from the parasite's egg, which looks like an adult.
Larvae differ from adult insects in small size and inability to reproduce.
They, like adults, feed on human blood. Before turning into an adult parasite, the larva molts.
It is necessary to distinguish between the concept of "nit" and "egg louse." Nn is the formation of eggs and a special sticky substance that serves to hold this design on the hair. If you look at the nits without special devices, it resembles the usual white stripe on the hair and can be mistaken for dandruff. Having examined the nits under a microscope, you will see a neat handbag, tightly wrapping the hair. For more information about lice, see this video:
Larvae are called insects hatched from eggs. After molting, they turn into nymphs.
The development of the first instar larvae takes from 1 to 10 days at a temperature of + 10 ... + 30 ° С. Hatching time does not depend on how often an infected person washes his hair. The hatching of the larvae occurs as follows: the insect pierces the shell of the nits with its jaws and actively breathes. When breathing, the parasite passes air through the entire digestive system and releases it through the anus. As a result, in the lower part of the nits creates a kind of air cushion, pushing the larva.
Once on the human skin, the insect begins to feed. After eating, the larva of the first age starts molting and turns into a nymph.
The period of development of the nymph of the first age is 5 days.
On the development of the nymph of the second age takes 8 days. After that, the nymph turns into an adult insect. Nymphs need three molts due to the fact that the chitinous cover on their body is not able to grow along with the soft tissues of the parasite.

Adult insects begin reproduction immediately after the first meal. Mating occurs within 1 to 2 days. For fertilization of all eggs in the body of a female louse, one copulation is enough. The life of an adult individual lasts 46 days. During this time, one female head louse is able to lay up to 140 eggs.
Pubic lice lay about 50 eggs, and clothes - up to 300.
Reproduction is significantly accelerated with a large number of parasites in the hair, as the females and males do not have to spend a lot of time searching for each other.
Features of different types of lice and ways to combat them
The life cycle of pubic and body lice differs little from that of the head ones. They differ only in their fecundity.
Body lice are the most prolific. Their development can take up to 50 - 60 days due to frequent washing of clothes and changing bed linen.
Pubic lice differ in relatively slow reproduction rate in different parts of the body. For more information on fighting the parasite, see this video:
Ways to control lice do not depend on the characteristics of their development and reproduction. Head and pubic parasites are excreted by special insecticidal agents.
Treatment is usually divided into several stages.
At the first stage, it is necessary to get rid of adults and nits in the hairline. It is advisable to cut hair short. Before using any means to combat lice, you need to carefully study the instructions, since most of these drugs contain enough toxic substances in their composition.
The most common and effective remedies for pediculosis:
- Medfoks,
- Foksilon,
- Medilis-super,
- Avicin,
- Pedilin
- Parasidosis
- Hygia
- Pedikulen Ultra,
- Pair Plus
- Here
- Paranit
- Nittifor.

Hair treatment should be carried out in a well-lit and ventilated area. After applying special tools you need to perform mechanical cleaning of hair from dead lice and nits. To do this, you can use both regular combs and special combs for lice sold in pharmacies.
A hot bath with soap and disinfection of clothes and bed linen will help get rid of lice.
Ways of infection
Lice are transmitted from one person to another in a contact way: just stand next to the carrier or use his personal hygiene products. At risk are people who:
- spend a lot of time in public places
- often go on long trips
- touch someone else's hair, clothes, hairbrushes, etc.
You can also become infected at the time of visiting any standing water body, as these insects are able to stay on the surface for some time.
One of the common misconceptions is that lice only appear in people who do not comply with hygiene standards. Practice shows that anyone, even the cleanest man, can infect with parasites.
We recommend to read: where did the lice on the head of a person.
Incubation period
 After a louse hits a human body, it lays an egg covered with a special substance. The shell protects the contents of the capsule from mechanical damage and exposure to chemicals. The whole structure is tightly fastened by a thread.
After a louse hits a human body, it lays an egg covered with a special substance. The shell protects the contents of the capsule from mechanical damage and exposure to chemicals. The whole structure is tightly fastened by a thread.
The development of nits on average takes seven days. Throughout the life of the egg goes without food and oxygen.
When the week comes to an end, a larva appears. She is unable to immediately leave the capsule, therefore, gnaws at her, while simultaneously accumulating carbon dioxide in the lower part of her body, which pushes it out. In appearance, it does not differ from the nits anything other than size.
How long the incubation period of pediculosis in humans lasts is available on our website.
Stages of development of the larvae
After hatching, the parasite attaches to the hair and begins to actively feed. The transition to the next stage of development can take from one to ten days. Over time, the larva begins to look more and more like an adult, but its size is still small, and the reproductive system is undeveloped. When the first stage comes to an end, the future louse drops the old chitinous shell and becomes covered with a more solid shell.
After this procedure, a nymph is formed, which passes through two stages of development. Each of them ends with a molt. The chitinous shell is not elastic, therefore, when it becomes too small, it is shed. The evolution of the nymph lasts five days. At this stage, the reproductive system is formed.
The transformation of nits into imago (adult) takes about 16 days. The term increases if living conditions are unfavorable.
Breeding features
 Parasites can begin to multiply within a few hours after the last stage of evolution. The mating process takes from 20 to 70 minutes. A female receives seed that is stored in the abdomen and used as needed.
Parasites can begin to multiply within a few hours after the last stage of evolution. The mating process takes from 20 to 70 minutes. A female receives seed that is stored in the abdomen and used as needed.
She does not need to get in touch with a partner again, since these reserves are enough for the entire life cycle. The male dies 7-10 days after mating.
The future larva forms very quickly, as it moves along the oviduct it is covered with a dense protective sheath. After 24 hours, the female sticks a nit to the hair or fabric, depending on the habitat. This happens as follows:
- The louse clings to the paws with a thread or hair with the help of claws located at the ends of the paws.
- It strains the abdominal wall and squeezes out a little sticky substance.
- From the back of the abdomen an egg takes out, which plunges into the already prepared place.
- Adhesive solidifies, forming a reliable shell.
How lice multiply, the speed of development, read on our website.
Important! It is much easier for parasites to multiply when their owner is not trying to get rid of them. The female does not have to wait for a suitable partner to appear, so the process of laying eggs goes faster. To stop the insect population in this situation becomes much more difficult.
How long live
Longevity usually does not exceed 46 days. This indicator may change up or down depending on the sex and type of animal.
Parasites survive by consuming the blood of their host 2 to 6 times a day. Without a power source, they cannot last more than 55 hours.
Lice never experience feelings of hunger, so draining blood for them is a way to calm down instinct.
As already stated at the beginning of the article, There are three types of lice that can live on the human body:
- Pubic - live on the hairy part of the pubic zone, scrotum. Less often - on the eyelashes, mustache, back, chest, beard.
- Payments - live on the skin (in the neck, shoulder blades, waist), in the folds of bed linen and clothing.
- Head - based on the scalp.

Parasites of the first type are transmitted mainly during sexual intercourse. The second and third - by household. Habitat and mode of distribution are not the only differences between species.
The size of the insect of the pubic type does not exceed 1 mm. Life expectancy for individuals of two sexes is 30-31 days. During this period, the parasite practically does not detach from the power source. The female lays larvae no more than 26-30 times over the entire period.
Hanging louse is the largest. The length of her body can be up to 5 mm. Male individual lives 4 weeks, female - 1.5-2 months. They eat 2-3 times a day. The female has time to make up to 295 clutches until she dies.
The head parasite species feeds twice a day. The duration of the life cycle does not exceed one month. These insects are of medium size - 2-4 mm. The female leaves the offspring about once every 6 hours, by the end of the term - 120-140 clutches.
One laying of pubic lice consists of 1-2 eggs, clothes 8-10, head - 2-4. The number of larvae that a female can lay depends on its size.
We recommend reading: what are the lice, their similarities and differences.
Terms of death
 Insects do not tolerate cold. They easily withstand a drop in temperature to zero, but at rates below 20 ° C they die within 30 minutes. Larvae capsules maintain normal performance.
Insects do not tolerate cold. They easily withstand a drop in temperature to zero, but at rates below 20 ° C they die within 30 minutes. Larvae capsules maintain normal performance.
To die from the cold parasite, maybe only if it is separated from the host organism. Therefore, to combat body lice wet clothes hang out in the cold.
The optimal temperature for the reproduction of parasites on the body is 30 ° C. With a significant deviation from this index ° C, females cease to make clutch, the development of nits slows down. When the figure reaches + 45-50 ° C, the adults die within half an hour, but the eggs remain viable.
The larvae are protected by a durable shell, so they are not afraid of the usual effects of low or high temperatures. They also continue to gradually develop after they fall into the water. To destroy them, it is necessary to create such conditions under which nits will be in a stressful situation due to sudden changes in the environment. This method is used for the treatment of lice clothes and linen: they are ironed or boiled.
At what temperature lice and nits die, you can find on our website.
Important! Changing the temperature regime is not suitable for getting rid of parasites living on the human body. In this case, the best way to create unfavorable conditions for the life of lice is to use special means.
Insecticides
Insecticides are chemicals designed to kill various insect pests. Usually they paralyze the nervous system of the animal, which ensures its quick death. But there are tools that work differently: they deprive the parasites of the ability to breathe. Drugs of the second type can not damage the nits, so they are used as one of the components of the complex.
 Acetic acid is a popular folk remedy for lice. In a mixture with water, it dissolves the substance by which the capsules with eggs are attached to the hair.
Acetic acid is a popular folk remedy for lice. In a mixture with water, it dissolves the substance by which the capsules with eggs are attached to the hair.
Acetic environment is also unfavorable for adults. They do not die, but lose the ability to hold tight. After such treatment, it is easy to get rid of parasites and their clutches during combing.
Insects are afraid of other organic acids: cranberry, lemon, grape juice.
Kerosene for removing lice was used in those times when there were no safer options. It was applied to the infected hair, a plastic bag was put on top and kept for 30 minutes. Kerosene poisoned adults and partially dissolved the capsules of the larvae, because of which they could not continue to develop normally.
Taking advantage of the smell, parasites find a source of food, a couple to produce offspring, so they are sensitive to strong odors. You can use this weakness if you add essential oils to the treatment products for the body and head. Best suited for this purpose:
In shampoo or water for rinsing hair, you can add up to 5 drops of essential oil, in the funds that are intended for application to the body - no more than 1-2. A strong smell will not kill the insects, but will make them rather sluggish, so that combing with a comb will bring maximum benefit.
What natural oils are effective against lice and nits?, as well as recipes for their use, read our website.
The easiest way to create an unfavorable environment for pubic lice is to shave off the hair on which they live. This method is also suitable for getting rid of parasites that live on the head, but modern medicine offers many tools that make it possible not to make such a sacrifice.
Effective shampoos for lice and nits:
- Paranit
- Veda and Veda-2,
- Nyx
- Hygia
- Pedikulen ultra,
- Nit free (nit free),
- Does tar shampoo for lice and nits help?
Pathways and stages of development
The spread of these insects is often due to visits by many people. pools or beaches, as the parasites are able to stay in the water for a long time, which only facilitates their entry into the hair of other people, especially those that neglect wearing swimming caps.
Another possible infection that characterizes the type of lice development is wearing the same headgear, especially for hats made of wool and other natural materials. Louse takes the structure of the cap by the hairline, so it moves into it and then infects another person.

Once on the hair, lice begin to lay eggs, which are called nits. About a week, in the presence of favorable conditions, the nit develops. Having reached a sufficient level of development, larvae hatch from eggs, which can grow to the state of a nymph from 1 day to 10 days.
Evolving over 1-2 weeks the nymph goes through 2 stages of development and ultimately takes the form imago - adult insect. A sexually mature louse again sets aside a lot of nits that are attached to the wearer's hair, thereby triggering the lice on a new life cycle.
The incubation period of the person, so sustained in tempo, makes the lice and nits in a person 2-3 months combing the head from unbearable itching, and also makes the infected pediculosis a dangerous peddler. In order to deter the breeding of parasites, nits are cleaned daily, and the head is often washed with a special shampoo.
Prevention
The incubation period for lice and nits is rather short and the first symptoms of pediculosis make themselves felt. after 2-3 weeks. As a rule, the disease is expressed in itchy scalp and leads to involuntary combing with the formation of bloody and festering crusts on the skin.
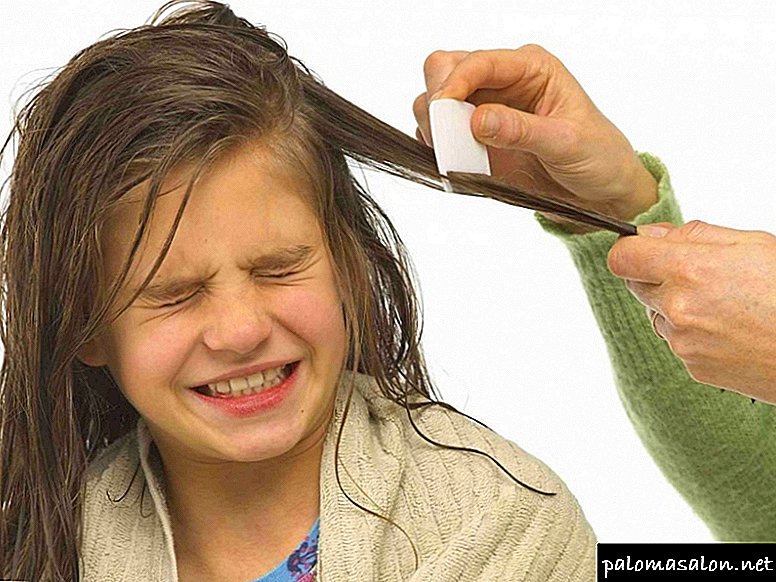

To avoid infection, it is necessary to reduce the number of contacts with possible carriers of parasites, as well as to avoid places with a large number of people who are there at the same time. Caught in a crowd or in a downtrodden public transport, it makes sense not to take off the headdressand you should not touch other people with your head.
Personal hygiene products, it is desirable to use only their own. Others hairbrushes can be a tool for direct introduction of lice on the hair of another head It also makes sense to check your sexual partners for parasites, as close contact with the heads during sex can cause infection with pediculosis.
After going through its life cycle, a human louse usually dies. If the infection is confirmed, then the lice, together with the nits attached to the hair, should be combed out every day, possibly several times. If the use of anti-pedicular products and shampoos does not help, it is customary to shave your head bald.
What is nits?
The louse living on the person, represents the small insect leading a parasitic way of life and eating its blood. The body of the parasite reaches 1.5-2 mm and has a grayish color. A saturated pest acquires a dark brown hue.
Insects of this species are dioecious. Females differ both in an internal structure, and appearance:
- female individuals are much larger than males, have a forked belly and a special spur on their hind legs,
- males are distinguished by a rounded abdomen and the presence of a claw-like outgrowth, due to which males retain their partners during mating,
- in the females almost transparent abdomen, spherical nits can be seen, in males a copulative organ is noticeable,
- the internal structure of the female and male genital organs is distinguishable only under a microscope.
Head louse is a small blood-sucking insect parasite that lives only on the human body and feeds on blood.
The insect develops very quickly, in just three weeks, thanks to a stable and comfortable living environment.
Stability is ensured by the fact that most individuals spend their whole lives on the body of one person, and comfort - the constant availability of food in free access (blood).
Every time, before moving to a new stage of development, lice shed.
This is due to the fact that the chitinous cover does not have time to grow with the body and, simply, is broken.
The molting process takes about 5 minutes.
Nits are eggs that are laid by female lice. They are attached to the hair of a person a few millimeters from the root with the help of an adhesive liquid that is produced by the sex glands of the insect.
The protective shell is so reliable that it is impossible to wash the eggs with water, even with the addition of shampoo. Nits have an elongated oval shape and look like translucent or yellowish-white seeds.
They are often confused with dandruff, until they begin to comb, because, unlike dandruff, removing nits from the hair is very difficult.
Finding out how fast they multiply and what is the life cycle of head lice, we understand that we need to start fighting with them as soon as possible.
Stage of the life cycle of lice and nits
As they mature, several stages of head lice develop:
- Egg. The duration of the first stage of the life cycle of a human louse is from 4 to 16 days and depends on the temperature and humidity of the habitat.
- Larva. After an incubation period, the larva hatches from an egg in a very interesting way. Unable to immediately get out of the cocoon, she begins to actively breathe as soon as she chews through the shell.
The air, passing through the insect's anus, accumulates in the lower part of the nits and pushes the larva out. Freed, the parasite should immediately be supported in order to literally in a day go to the next level.
The life cycle of lice is illustrated in this picture:

Where and how long do lice live?
How long do lice live on the hair and outside the head? This type of parasite can live only in the scalp of the human head, as well as on the eyebrows and eyelashes. The louse is well suited for living in such an environment.
The claws on the end of the short legs help it not to fall down during movement, and the hooks located on the skin fold around the mouth - during feeding. With the help of a special bifurcation at the end of the abdomen, the female holds her hair while laying eggs.
On the sides of the body are 14 holes, through which the insect receives oxygen. When the owner washes his head, the holes overlapdefending the life of a thoughtful creation.
Due to its small size (2-4 mm) and flattened form, the parasite able to go unnoticed for a long time. Interestingly, lice can change color, adapting to the hair color of the wearer.
Most bloodsuckers feel comfortable at a temperature of 30 degrees Celsius and 70% humidity. Under these conditions, they move quite briskly — the speed reaches 25 cm per minute — and develop rapidly.
Head lice are able to feed only on human blood, which no other food can replace. In order to grow and multiply rapidly, bloodsuckers need to eat 2 to 6 times a day.
A hungry insect is able to live a couple of days and soon dies.
The century of the parasite is short and lasts about a month. In comfort conditions the insect is capable live up to 46 days. Female head lice live twice as long as males and drink three times more blood per meal.
Reproduction rate

Having reached the imago stage, the insect mates for two days.
A few hours after mating, the louse starts breeding - it lays its eggs, 2-4 pieces per day.
Also, the parasite can lay empty eggs without mating.
During the life of the insect produces light about 150 new individuals.
Thus, if at least one insect has run across the human body, in a month there will be hundreds of them.
Basic information about lice infestation
Lice can not jump or fly, so infection occurs only when close contact between two people - directly or through shared items. Despite the awkward appearance, insects move at a speed of 20 cm per minute, so it is quite easy to catch pediculosis.

Lice can live on a household item from several hours to two days and wait for the new owner. Insect for some time does not die in the water, so you can catch pediculosis, swimming in natural and artificial reservoirs.
Despite the fact that pediculosis is known to man since ancient times, there are still a lot of myths about the ways of infection with this disease.
Three main myths
In temperate latitudes, head lice do not tolerate the disease, although infection can enter the body through scratching.
The real distributors of disease are only body lice - they are able to tolerate typhus.
Lice that live on animals and birds are absolutely safe for humans, as they are adapted to life only on their host. Cat lice live on cats, dog lice on dogs and so on.
Human lice do not go to animals, because pets do not need to be processed if a pediculosis patient appears in the family.
Another common misconception is subcutaneous lice, which in reality does not exist. In ancient times, people knew little about the pathogens of various parasitic infections, so they thought that lice were also responsible for scabies.
Pathways of parasites
Lice - insects are quite vulnerable and sedentary, with a low reproduction rate. Nevertheless, in speed of spread they overtake many parasites. How do they do it? Lice simply crawl from one person to another, taking advantage of the situation when people are in close physical contact.

Because of this method of spreading pediculosis occurs primarily in places where people are crowded, cramped. Especially quickly parasites spread in communal apartments, barracks, camps, kindergartens, schools, dormitories.
Ways to spread parasites:
- move from person to person during sleep in one bed, with joint activities,
- carried on objects and clothing
- fall on the bedding, clothes and pillows, and from there they fall on the head of a healthy person,
- during sexual intercourse, two types of lice can be transmitted at once: head and pubic,
- parasites can survive in water for up to two days, therefore they can be transmitted when bathing.
Lice are not transmitted at a distance, so you can safely communicate with a person suffering from pediculosis. However, even with short-term close contact (kiss, hug), the insect can crawl onto the head of a healthy person.
Stages of development of causative agents of pediculosis

For many years I have been studying intestinal problems, in particular salmonellosis. It is terrible when people do not know the true cause of their diseases. It turns out that the whole thing in the bacteria Helicobacter Pylori.
These bacteria are able to live and reproduce not only in the intestine, but also in the stomach. Being introduced deep into its walls, the larvae are distributed through the whole body by the blood flow, getting into the heart, liver, and even into the brain.
Today we will talk about the Notoxin natural product, which turned out to be incredibly effective in treating salmonellosis, as well as participating in the federal program “Healthy Nation”, thanks to which the product can get for FREE when applying until November 27th.
Head lice live on the scalp and feed on human blood. Most of the parasites have developed a special mechanism for adapting to the absence of the host - developmental delay. Lice do not have this mechanism. They are always supplied with food, develop without delays and are able to multiply quickly.
The development of lice consists of several stages. The duration of each stage depends on the temperature and can vary by 1-2 days upwards or downwards.

In the first stage, insects lay eggs. They stick their nits to the hair with a sticky secret. In composition and strength, it resembles cement.
Eggs ripen 9 days. Young lice hatched from eggs are called larvae. They are small and cannot reproduce.
Growing larvae takes 9-12 days. During this time they molt twice.
Larvae feed every 2 hours. The person at the same time feels an increasingly severe itching, pediculosis takes on a pronounced form. With each molt, the larva grows in size until it reaches the size of an adult insect.
After the last molt, young females mate and in a few hours start laying eggs. One mating is enough to fertilize all the eggs. Partners will no longer be needed by females - they will lay a viable egg for another month without any male participation.
Life cycle of pubic and body lice
The development cycle of parasites who prefer the intimate area is similar to head lice. Pubic parasites settle on areas of the body covered with more sparse hair than on the head. These are the areas of pubis, underarms, eyebrows, mustaches, beards, eyelashes.
The body louse lives on clothes and bedding. She leaves her shelters only to eat. Eggs parasite sticks to clothes and downy hair on the human body.
The insect lives on average 48 days, the life cycle duration is 16 days. The female has time to lay about 400 eggs.
1 The root cause of the disease
It is a mistake to believe that the presence of lice is a sign of social distress, terrible living conditions or non-compliance with personal hygiene. Louse can appear in the most successful and clean person.
He'll just get head lice and won't even suspect it. The first signs will appear only in a few weeks, when the number of parasites living in the hair will increase significantly.
Reproduction of lice occurs very quickly.
Most likely to pick up the parasite in public places, such as school, kindergarten, boarding school, etc. It can happen anywhere. Pediculosis is transmitted from an infected person to a healthy and indirect way through the general use of certain personal items, such as a comb, hat, towel, pillow, clothing, etc. With direct infection, the parasites simply jump from one head to another and at the same time quickly multiply.
On the human body can live different types of lice:
Each species has its own life cycle. The pubic parasites reproduce most rapidly, and the slowest in this sense are the head insects. But each of them can live up to 2 months, it all depends on the environmental conditions, how optimal they are.
It is believed that pediculosis is common only among those individuals who lead an asocial lifestyle and do not follow the rules of personal hygiene. However, this opinion is erroneous, since even rich people living in luxury have head lice. Where do these insects come from? What are the causes of head lice infection? These questions are of great concern to many.
The most common infection occurs in kindergartens, schools, boarding schools and other public places. Indirect transfer of pediculosis is carried out from patient to healthy with the general use of one comb, the exchange of hats, scarves, hair accessories, as well as through towels, pillows, garments and so on.
If a person has head lice, the reasons for their appearance will not necessarily be associated with a violation of hygiene. You can pick up a parasite anywhere.
They crawl from one head to another by direct contact, as head lice are transmitted in this way, because they do not know how to fly or jump. The most frequent infection is carried out when visiting baths, saunas, swimming pools, using bed linen in train cars, etc.
Considered parasites live relatively short. There are 3 main types of insects - head, pubic and clothes.
Their existence and reproduction practically do not differ from each other, except for localization. Head parasites are most common in children, dressing - in people with unsanitary lifestyle, pubic - in 8% of the population.
Reproduction and development is as follows: an adult female lays nits. From them larvae appear, then nymphs are formed, and from them adult individuals turn out.
The maximum lifespan of the parasite is 46 days.
It is a mistake to believe that the presence of lice is a sign of social distress, terrible living conditions or non-compliance with personal hygiene. Louse can appear in the most successful and clean person.
He'll just get head lice and won't even suspect it. The first signs will appear only in a few weeks, when the number of parasites living in the hair will increase significantly.
Reproduction of lice occurs very quickly.
Lice are permanent human ectoparasites. There are about three hundred species of such insects known in the world; 15 genera and 41 species live in Russia.
They all do not know how to fly or jump, they move only by running. Therefore, infection can occur only in close contact with the sick.
Most often, children attending kindergartens and school suffer. They constantly interact with each other: kids play, exchange toys, hats, personal hygiene items (combs and towels, for example).
An adult can get head lice from their own child, in a barbershop, in a public bath, on a train, in a hospital. Certain types of insects live in the folds of clothing, from there then they transfer to the skin of the body.
Distribution of pubic parasites occurs during sexual intercourse. Their eggs in the external environment retain their viability during the week, therefore it is considered possible to use a contact-household transmission path.
Head Lice: Causes of Lice
It is believed that pediculosis is common only among those individuals who lead an asocial lifestyle and do not follow the rules of personal hygiene. However, this opinion is erroneous, since even rich people living in luxury have head lice. Where do these insects come from? What are the causes of head lice infection? These questions are of great concern to many.
The most common infection occurs in kindergartens, schools, boarding schools and other public places. Indirect transfer of pediculosis is carried out from patient to healthy with the general use of one comb, the exchange of hats, scarves, hair accessories, as well as through towels, pillows, garments and so on.
If a person has head lice, the reasons for their appearance will not necessarily be associated with a violation of hygiene. You can pick up a parasite anywhere. They crawl from one head to another by direct contact, as head lice are transmitted in this way, because they do not know how to fly or jump. The most frequent infection is carried out when visiting baths, saunas, swimming pools, using bed linen in train cars, etc.
Distinctive features of lice
First you need to figure out which species of blood-sucking insects affect a person:
Representatives of the first two groups belong to the same morphological type of human louse. As a result of evolution, the parasites were divided into separate subspecies, which was provoked by differences in lifestyle.
But in appearance, the representatives of these morphotypes are similar. So, the larva is a lot like an adult louse.
Insects at different stages of development have the same body shape, number of paws and common external features.
However, there are differences, for example, body length. The sizes of lice larvae vary from 0.7 to 2 mm.
The length increases with the growth of the insect. Body color at the initial stage is slightly different.
Adults are characterized by a light brown color. The larvae are almost white.
However, after the first meal, the color of the growing insects immediately changes to darker. The body of the head and body parasites is characterized by an elongated shape.
Due to the light color of the larvae, it is difficult to determine what kind of white grains on the hair: lice or dandruff. Complicates the task and the small size of insects at the initial stage of development.
To make sure that lice infestation has occurred, it is necessary to evaluate the symptoms in the complex. Larvae of head parasites live exclusively on the head.
Representatives of another morphotype of human lice (ward individuals) colonize things, and feed on the body. However, insects do not stay here for long, but return to clothing.
The larva of the pubic louse is also very similar to the adult, but the size of insects of this species is slightly different. This is due to the fact that parasites have a rounded body shape.
If the adult reaches 2 mm, the larva after emergence from the egg is characterized by even smaller sizes (about 1 mm). The color of insects of this species is also light and subject to change during the meal.
Thus, the body acquires a red tint due to the blood that feeds the parasite. They are found in pubic lice in the groin area, less often lashes, eyebrows, mustaches and beards, as well as underarms.
The size of this type of parasite is on average about 5 mm, female individuals are slightly larger than males. The clothes louse, like other similar parasites, cannot live in the environment for a long time, and almost immediately perishes. Under these conditions, life expectancy is 3 days, at low temperature - 7 days.
What distinguishes lice from other parasites is that they are insects with an incomplete transformation. From the egg emerges a larva resembling an adult, but it is smaller and cannot reproduce. Food in this case occurs due to human blood, after which the larva molts 3 times and becomes an adult.
Nitrogen and egg lice - different concepts. Nit - a kind of cocoon. Egg formation comes from a sticky substance.
Larvae of lice resembling adults are nymphs. This stage is in other parasites - bugs, cockroaches. The incubation period does not last long. The lifetime of lice is also short. Reproduction speed, on the contrary, is impressive. Experts define the larva after molting as a nymph, and the insect that has emerged from the egg, like a larva.
The incubation period for the development of head and wrap lice is almost the same. Nymphs in a louse hatch after 5 days. The average growing time is 3 weeks. The head parasite is identical.
Lice cause serious discomfort to humans.
Important! Nits in lice do not hatch. Nymphs hatch, nits are deposited by an adult. From nits get the larvae. For pubic parasites, incubation is 6 days. The larva develops in 18 days. The adult individual lives only a month, the female is able to lay up to 50 eggs. Of the nits in the pubic parasites, the larvae will not appear if the temperature is less than 22 degrees.
As already mentioned at the beginning of the article, there are three types of lice that can live on the human body:
- Pubic - live on the hairy part of the pubic zone, scrotum. Less often - on the eyelashes, mustache, back, chest, beard.
- Clothes - live on the skin (in the neck, shoulder blades, waist), in the folds of bed linen and clothing.
- Head - based on the scalp.
Parasites of the first type are transmitted mainly during sexual intercourse. The second and third - by household. Habitat and mode of distribution are not the only differences between species.
The following types of lice can attack people:
The bites of all insects are accompanied by severe itching, the consequence of which are strong scratching. In addition, the probability of the spread of dangerous infections.
Three types of parasite can parasitize on our body:
- Pediculus humanus capitis - head louse.
- Pediculus humanus corporis - a clothes louse.
- Phtyrus pubis - pubic louse.
Depending on what type of patient is infected, a head, ward, or pubic lice (ICD-10 B-85) is diagnosed. There are cases when two or three insect species parasitize on the body at the same time. Then it is a mixed type infestation.
Head louse
How fast do lice breed? Let's look at some of their views:
- Clothes (so-called wearable). They carry out their livelihoods exclusively in places such as beds, sofas and clothing.
- Head. They chose the scalp of a human head (beard, mustache and hair).
Important! Head louse is less dangerous for mankind compared to the closure, as it is not a carrier of such a terrible disease as typhus.
- Pubic (or ploshitsy). They live on the external genitals and cause itching and burning in this place.
On a note! Each parasite species has its own life cycle. But head lice reproduce most slowly, and pubic insects are fastest.
There are 3 main types of lice:
Head parasites often infect children, so they are found in camps and school institutions. Nits are firmly attached to the hair. Girls are infected more often than boys, but hygiene does not affect it. Lice can appear even because of short-term contact with the carrier of parasites. Sometimes they can be found even in those who regularly wash their hair with shampoos.
Head parasites often infect children, so they are found in camps, school facilities
Louses on the contrary are found among those who lead an unsanitary way of life. Nits cling to clothes and ripen there under the influence of body heat. If you do not change clothes, you can become a carrier of such lice.
Pubic parasites or plosschitsy (from the Latin Phthirus pubis) - the last species. About 8% of the population is infected with this type of louse. The oral apparatus is piercing-sucking, the body is flattened, the insect has a chitinous cuticle. The whole cycle of life takes place on the host, outside of which the parasite cannot live.
You may also be interested in the article "Sexual or pubic lice: ways of infection and treatment methods."
Body lice are found in those who lead an unsanitary lifestyle.
In appearance (morphology) of imago, Head louse (Pediculus humanus capitis) is close to the described species. She is smaller than a clothes louse. In addition, the segments of the abdomen of the head louse are separated by deeper grooves, the sickle-shaped appendages at the posterior end are more obtuse at the bottom, and dark pigmented spots are often located on the sides of the chest and abdomen.
In addition to the described species, the Pubic Louse Phthirus pubis, which is also similar in morphology to adult louse (Pediculus humanus humanus), is often found.
The life cycle of the parasite
Lice spend their entire lives on the scalp of a human head. If uninvited guests leave human hair in any way, they die within 1-2 days. Such insects cannot exist on animals.
To assess the rate of lice development, it is important to know how quickly head lice multiply. The development cycle of the insect is 30-40 days, during which time the louse manages to set aside 2-3 hundreds of nits. Lice eggs are small translucent or white-yellow seeds, similar to sesame seeds. As a rule, the female fastens the larva in the root part of the hair, about 5 mm from the skin surface. After 10 days, young individuals hatch out of eggs - nymphs. During this time, the hair has time to grow back a bit, so all the nits, located more than 1 centimeter from the skin, are already empty.
After 2 weeks the nymphs turn into adults capable of laying eggs. With each new offspring, reproduction of head lice is becoming more and more spontaneous. The sooner pediculosis is detected, the easier it will be to get rid of it. The main thing is to be able to recognize it by symptoms.
Signs of Pediculosis
Here they are, head lice. Where the parasites come from, we already know, now let's figure out how this problem manifests itself. The main symptoms of the disease include the following:
- Itchy scalp. Most often, the discomfort is manifested behind the ears, in the neck and neck. Itching acts as a peculiar allergic reaction to insect saliva. In the first weeks after infection with parasites such as head lice, symptoms in the form of itching, as a rule, do not appear. An unpleasant sensation arises after the first nymphs hatch from the eggs and begin to look for a “feed” for growth and livelihood. When a sufficient amount of louse saliva accumulates in the layers of the epidermis, an itch will appear.
- The presence of lice in the scalp. Parasites can be seen, although they are quite difficult to detect: they are small, they move very quickly, and are almost indistinguishable in hair without an additional source of light.
- The presence of nits on the hair shafts. Lice eggs are mounted on the hair, besides successfully masked by its color. The most common place for attaching nits is around the ears and along the hairline on the neck. Often the lice larvae are confused with dandruff, dermatological diseases of the scalp, which significantly complicates the diagnosis of lice.
When should I see a doctor?
If your child or another family member has a head louse, treatment should be started only after consulting a doctor. Studies show that many patients were treated with insects with drugs or home remedies at a time when the parasites were not active. Moreover, sometimes nits can be confused with dandruff, remnants of cosmetic products on the hair (for example, varnish), dermatological diseases of the scalp, empty nits left from a previous infection with pediculosis, and so on.It is harmful to treat the head unnecessarily, since almost all the drugs for lice are toxic and have various side effects.
How to remove head lice?
For all the time that a person is familiar with lice, they have tried many methods of destruction from these insects. Lice head - very tenacious parasites, so the usual shampoo to get rid of them will not work. Effectively deal with parasites can be drugs and folk remedies.
Drugs that kill lice and fleas contain substances called insecticides. Among such means - "Permethrin", "Malathion", "Cypermethrin", "Fenotrin" and others. Unfortunately, the use of medications containing the above substances can be dangerous to humans. Therefore, wondering how to remove head lice with these drugs, you should carefully study the instructions and follow all the prescribed recommendations.
If you have a head louse, treatment can be carried out by less toxic means (for example, vinegar, kerosene, hydrogen peroxide). Such methods also have their drawbacks: if used improperly, you can face a chemical burn of the scalp, baldness or baldness. Parasites can be combed thick comb, which is used specifically to combat lice. Now, such ridges are not cheap, but this method of removing lice has no side effects. However, in order for it to bear fruit, you should spend a lot of time and effort.
Lice Remedies
In the treatment of pediculosis, people are concerned about the question of which remedy for head lice is the most effective and at the same time safe. After all, if we expose the scalp to chemical attack by aggressive substances, then we want the result to be high. To combat parasites used aerosol preparations, sprays, lotions, special shampoos and mechanical means (for example, combs for combing nits and lice). Each option has its pros and cons, contraindications and features of the application.
Sprays against pediculosis
The most effective drugs for lice and nits include funds "Para-Plus" and "A-par." These aerosols are intended for the treatment of linen and clothing for pediculosis. Some of them are suitable for treating the scalp. To achieve good results, it is recommended that things, linen (especially in the seams and folds) and the head be processed at the same time to avoid re-invasion.
The composition of the aerosol "A-steam" includes piperonyl butoxide and esdepalletrin. The preparation does not leave stains on clothes, and the things processed by it do not need the subsequent washing. However, such things can not be used immediately: first, they should be ventilated before use, and they can be washed in 2-3 days, not earlier.
Precautions include treatment with open vents. In case of contact with eyes, rinse thoroughly with water. The instructions noted that the uncontrolled use of hair treatment products is undesirable because it is very toxic. It is not recommended to spray it near other people with asthma, children, pregnant women. The components of the drug may be an allergic reaction, often there is lacrimation, burning of the mucous membranes, sore throat.
A safer drug against pediculosis is Para-Plus aerosol. The active ingredients in him are permethrin, malathion, draned butoxide. Despite the fact that Para-Plus is considered a more benign remedy for killing lice, its action is very effective. The aerosol is sprayed directly onto the hair and scalp, after treatment the hair is not covered.
After 10 minutes, you should wash your head with ordinary shampoo, and comb out dead lice and nits with a thick comb. Linen, clothes, combs also need to be treated with the drug to avoid reinfection. The tool is not recommended for children under 2 years of age, people with asthma, who are sensitive to the active components of the aerosol. Leave the product on the hair for more than 10 minutes is also not worth it, otherwise there may be risks of chemical burns.
Nits and Lice Sprays
Parasites are effectively eliminated by using sprays such as Pediculen Ultra, Paranit and Nuda. These drugs are well proven and have high efficiency. They are an oily, odorless, oily, yellowish liquid that first paralyzes parasitic insects and then kills them.
"Paranit" (spray) is applied to dry hair, and when it is fully moisturized, the product is rubbed into the hair roots. If the curls are rather thick and long, then they are combed out by separate strands. The product is left for 15 minutes, and then wash your head with warm water using regular shampoos. Dead lice and nits should be combed with a thick comb. After that, the head is washed again with a special “Paranit” shampoo, and if necessary, repeat the procedure in 7-10 days. Contraindications to the use of the drug are:
- age under 3 years
- dermatological diseases
- hypersensitivity to spray components,
- pregnancy and lactation period.
Spray "Nuda" has a highly effective anti-pediculosis effect. Just like Paranit, the drug is allowed to be used by adults and children over 3 years old. It is sprayed onto dry hair and then rubbed into the roots. The exposure time for parasites is 45 minutes, after which the hair is thoroughly washed with regular shampoo and combed out with a thick comb, which is sold complete with a Nyud spray.
A pedicle for combing dead nits and lice is provided with Pediculen Ultra. Its difference from the above preparations is that it cannot be used for children under 5 years of age. The active ingredient is anise oil of 6% concentration.
To destroy the head lice, the hair is abundantly moistened with the preparation, carefully rubbed into the skin, and after half an hour it is washed off first with clean water and then with the help of a shampoo. When re-invasion procedure is repeated. It is necessary to work in gloves, if the patient uses contact lenses, they must be removed before the treatment begins. Contraindications are the same as those described above.
Shampoos as a remedy for head lice
Compared to aerosols and sprays, head lice shampoos are less effective agents that belong to the group of insecticides of phosphoorganic origin. The principle of action of such drugs lies in their deep penetration into the body of the parasite, as a result of which they die. These products include Pedilin, Parazidoz shampoos and others.
The product is applied to wet hair, carefully rubbed into the skin and left on the hair for 5-10 minutes. After that, the hair is thoroughly washed and combed thick comb. A week later, the procedure must be repeated.
It is important to remember that shampoos against pediculosis are used only on prescription and for children older than 3 years. Pregnant and lactating women should not use such tools, and people who are sensitive to the active ingredients of drugs should be used with caution.
Chemerichnaya water against head lice
Head lice are susceptible to elimination by using the cemeric water. This fluid is a drug that not only fights parasitic insects, but also has a beneficial effect on the hair in general. The composition includes ethyl alcohol and rhizome extract of hellebore Lobel.
Chemerichna water is sold in pharmacies in bottles. Reviews let you judge him as an effective drug against lice. In addition, the price of the product makes me happy - only 25 rubles per 100 g bottle. Alcohol tincture is applied to the scalp. When biting through lice of soft tissues, a drug that has a destructive effect on the parasite's organism also gets into its digestive system. The disadvantage of the tool is its low effectiveness against nits. The drug is contraindicated in people prone to allergies, pregnant women and children.
Folk remedies for pediculosis
Sometimes it is not possible to eliminate the problem with pharmaceutical preparations. As a rule, such cases include infection in pregnant or lactating women, as well as young children up to 3 years. There are many recipes to help beat head lice. Treatment with folk remedies, of course, is less effective, sometimes it may take more than one treatment procedure of the head, but these methods are safer for humans.
Acetic water is used to etch adult parasites and their offspring. For the preparation of funds required to take in the same amount of vinegar and hot water (the temperature of the latter should be about 60 degrees). The components should be mixed, the resulting solution to process the scalp, then the hair is covered with a plastic bag and wrapped with a warm towel. After half an hour, the hair can be washed with regular shampoo and combed out with a thick comb. With a strong infection, the procedure is repeated several times for two or three days in a row.
Dustov soap has the same effect. They wash their heads instead of shampoo, and, as a rule, after the first use there is a complete destruction of lice and nits. In order to exterminate the parasites on the head, you can use cranberry juice, which has a stunning effect, kerosene (it is applied along the entire length of hair from horses to ends). After skin treatment, the head is wrapped, leaving the product for 2-3 hours, and then the hair is thoroughly washed with shampoo several times, the dead insects are combed out with a comb.
Such plants as mint, pomegranate, geranium, burdock, onion, garlic, cumin and others are widely used to kill head lice. Burdock is used in the preparation of decoctions for washing the head, instead of it, you can use the roots and stalks of the devèce. Medicinal raw materials finely chopped (or take the dry ingredients in the pharmacy), pour water and boil. Then the broth is allowed to infuse and filter.
Geranium oil is mixed with ordinary shampoo, applied to the hair along the entire length, rubbed into the scalp and left for an hour. After that, still soaped hair comb combed. Then the agent is washed off. For rinsing in a liter of water, add a few drops of oil and wash hair.
A good therapeutic effect gives a mixture of decoction of mint and pomegranate juice. From the leaves of mint they prepare a concentrated decoction, mix it with the juice of pomegranate in the same proportions and rub it into the scalp. After that, the hair is wrapped with a warm scarf, and after 2 hours it is washed off in the usual way.
Useful videos
Pediculosis: pathogen, routes of transmission, complications, incubation period, species.
Pediculosis. How to get rid of lice.



